Methods for the detection of microorganisms
A) culture of biological fluids
Culture is a method for detecting microorganisms in various biological fluids. The sample to be tested is “laid” in a petri dish – a special plastic or glass container containing nutrients. There are many nutrients, always based on agar and enriched with other elements such as amino acids, salts, etc. The microorganisms grow in nutrients in 1-3 days and form colonies, which allow the identification and quantification of the microorganism. If no or very few colonies grow, the culture is considered sterile, in other words the test sample is reported to be germ-free. Conversely, if 3 or more different types of germs develop then the sample is considered to have been infected and the culture is repeated in another sample. There are many microorganisms that are detected by aerobic culture such as staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. Coli and others.
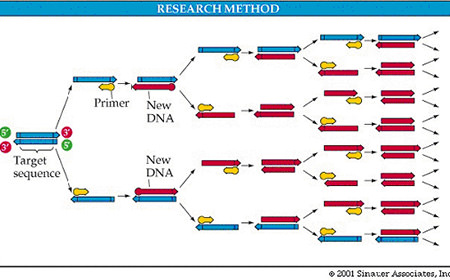
B) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) method
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) or the more advanced form of Real Time PCR is a method of biochemistry and molecular biology that can amplify the genetic material. By PCR a specific region of the genetic material can be multiplied up to billions of times. PCR method is used in the diagnosis of genetic diseases and for the detection of infectious diseases. PCR detects common bacteria more accurately, such as mycoplasma and ureaplasma. Mainly with this method viruses, such as the wart virus (HPV), the cytomegalovirus (CMV), the herpes virus (HSV) etc can be detected. In addition to the semen sample other biological fluids or cell smears may be used, such as sample from the cervix or the vagina.
C) Detection of intracellular pathogens (SPI Test ™)
The SPI Test ™ (Sperm Pathogen Immunophenotyping test) is a new diagnostic method, used for the first time worldwide for the detection of pathogens within spermatozoa and other cell populations. Detection of intracellular pathogens, such as chlamydia and viruses (HSV I / II, CMV, EBV) is achieved using immunofluorescence and flow cytometry.
More specifically, for the SPI Test ™ the cells are first fixed, holes are drilled in the membrane and then a special treatment follows. They are then incubated with antibodies – specifically for the microorganisms to be studied – and then the intracellular expression of the microorganisms is analyzed and evaluated by flow cytometry, in a large cell population.
The SPI Test ™ is used to detect chlamydia and viruses, such as cytomegalovirus (CMV) and herpesvirus (HSV), in biological fluids or cell swabs, such as a sperm sample or cells from a woman’s cervix.
The SPI Test is protected by copyright legislation and is provided exclusively at Locus Medicus and Zeginiadou-Andrology laboratories.
“Title AL:” INVESTIGATION METHOD OF PRESENT intracellular infectious agents to cells SPERM “Application No. 20120100185, filed on Industrial Property Organization from 29.03.2012 to award number 1008033. Deposited European Patent Number / Deposit Date EP 13721796.4 / 24.10 .2014 and title “METHOD OF INTRACELLULAR INFECTIOUS AGENT DETECTION IN SPERM CELLS”. International Patent filed with Number / Date of filingPCT / GR2013 / 000016 / 29.03.2013. “

General Information
more
Detection of HPV, HSV, CMV viruses
more

Aerobic – Anaerobic Microorganisms
more